3. Biochemical facilities used in biochemical testing machines
As it is known, biochemical testing machine uses the photoelectric colorimetric method, to measure the absorbance of the substances in the specimen, one cannot directly measure those substances because the substances themselves in the solution are crystal-clear. On the other hand, there are so many different substances in the test solutions that it is more difficult to measure and calculate. Therefore, to work with a substance that needs to be studied in a test solution, a colorimetric method is used. By using a chemical product of the substance to be studied, people use that substance to react with a certain substance or substances, in the reaction process, that substance will create an adsorbent product. Light at a certain wavelength is the strongest. The strong or weak absorption will be proportional to the concentration of that substance in the solution. From there we can calculate easily to get the desired parameters. The following will outline the principles for creating products with such absorption properties to measure some typical test parameters.
3.1. Creatinine (CRE)
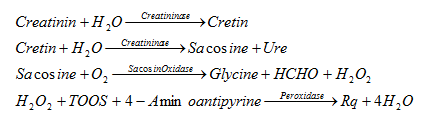
The coloring to measure Cre follows the following reactions:
Of which TOOS is N-Ethyl-N- (2-Hydroxy-3-Sulfopropyl) m-Toluidine
Pq is red in color, so when measuring requires 555nm wavelength
3.2. Total protein (PRO)
Cu ++ solution is an alkaline solution that reacts with the peptide chain of proteins to form a purple polipeptide complex. Measuring the absorption of this solution at a wavelength of 540nm will give the concentration of protein in the solution
Reaction equation:
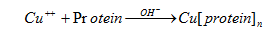
3.3. Urea
Ammonium and CO2 are created when urea is hydrolyzed with urease as a catalyst. The generated ammonium ion combines with 2-Oxoglutarate and NADH with the catalysts of Glutamate dihydro (GLDH) to form Glutamate and NAD +, the NADH / NAD reaction creates a linear change in absorption at 340nm wavelength, it is the ratio of with urea concentration in solution.
Reaction equation:
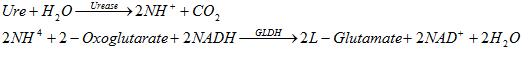
3.4. Cholesterol (CHO)
Cholesterol reaction according to the following reactions:
Rq is the red solution, measured at wavelengths of 492 to 550nm

Rq is the red solution, measured at wavelengths of 492 to 550nm
3.5. Glucose (GLU)
The coloring reaction for glucose is as follows:
Rq is the red solution, measured at wavelengths of 492 to 550nm, preferably at 500nm.
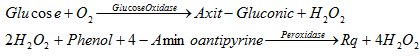
3.6. Whole bilirubil
Sulfanic acid reacts with sodium nitrite to form diazotized sulfanilic acid. This acid reacts with total bilirubil with the dimethylsulfoxide catalyst to form azobilirubil, which is measured at a wavelength of 540 to 560 nm, preferably at 555nm.
3.7. Amylase
In the reaction, amylase plays a catalytic role. The reaction speed depends on the concentration of amylase present in the solution, the product creates strong absorption at the wavelength of 400-420nm, preferably at 405nm.
Reaction equation:
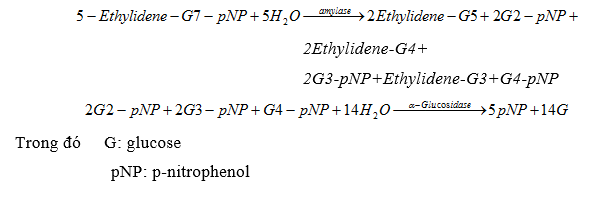
3.8. Creatininkinase (CK)
The reaction equation for creatine phosphate is as follows:
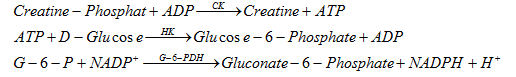
HK: hexokinase
ATP: Adenosine tri-Phosphate
G-6-PDH: Glucose-6-Phosphate dehydrogense
NAPD: Nicotinamide adenine denucleotide phosphate
The reaction for NADPH and G-6-P has an increase in absorption at the wavelength range 340nm (334-365nm) giving us the activity of CK in the sample.
3.9. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Measure the activity of LDH according to the following reaction:
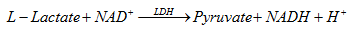
Measuring LDH based on the above reaction rate, LDH plays a catalytic role, reflected by absorption at 334-365nm.
3.10. Phosphate
Phosphate acid (ACP):
The presence of phosphate acid in the serum decomposes a-naphthyl phosphate into a-naphthol and inorganic phosphate. a-naphthol continues to decompose under the Fast red TR catalyst to give a dark yellow solution. Measuring the change of this solution at 405nm gives us the activity of this acid.
Alkaline phosphate (ALP):
ALP is present in p-Nitrophenylphosphate hydrolyzate (PNPP), in the process of releasing p-nitrophenol and phosphate, the increase in absorption at 405nm will tell us the activity of ALP in solution.
The equation for hydrolysis reaction is as follows:
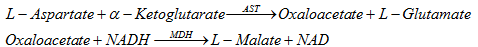
MDH is Malate dehydrate, AST acts as a catalyst for oxaloacetate, oxaloacetate produces NAD adsorbed at 340 wavelengths for AST activity.
ALT (GOT):
ALT acts as a catalyst for pyruvate formation:

3.12. Triglycerides (PAP)
Triglycerides in solution are hydrolyzed under lipoprotein lipase (LPL) to Glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol works with ATP with Glycerol Kinase (GK) catalyst to create glycerol-3-Phosphate G-3-P, G-3-P oxidized, light red solution absorbs well at wavelength 505 (490) -550nm).

3.13. Uric Acid
Uricase converts the uric acid present in the solution to allantoin, carbon dioxide CO2 and hydrogen peroxide H2O2. Under the catalysis of POD, Phenol derivative, 3,5-Dichloro-2-Hidroxy-benzenesulfonic acid (DHBS) and 4-Aminoantipyrine, H2O2 gives a slight red solution that can be measured at 520nm, increasing absorbance. corresponding to the concentration of uric in the solution.
Reaction equation:
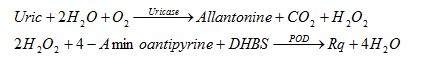
Hotline